Abstract
Introduction:
Hemophilia B (HB) is a X-linked bleeding disorder characterized by the deficiency in coagulation factor IX (FIX). Replacement treatment with recombinant human FIX (rFIX) is a safe approach to prevent bleeding in HB patients. There is an emerging concept that FIX resides extravascularly, by potentially binding to collagen IV in the subendothelial basement membrane, where it contributes to hemostasis. Our work evaluates hemostatic efficacy of extravascular FIX using animal models of tail clip bleeding and ferric chloride (FeCl3)-induced thrombus formation.
Methods:
The pharmacokinetic (PK) profile of wildtype rFIX (rFIXWT) and rFIX mutants which are stated to have an enhanced (rFIXK5R) or reduced (rFIXK5A) binding to components of the extravascular space (EVS) was evaluated in C57BL/6J HB mice (B6.129P2-F9<tm1Dw1s>). Blood and liver samples were collected at 0.08, 24, and 72 hours after tail vein administration of rFIX proteins (n=3-5 per timepoint). Plasma activity levels of rFIX were determined by a one stage clotting assay (OSCA). The content of FIX in the liver sections was analyzed using immunofluorescence staining. The direct binding of rFIX to collagen IV was evaluated for the first-time using surface plasma resonance (SPR). The in vivo efficacy of these proteins in HB mice was compared in tail clip bleeding and FeCl3-induced thrombus formation models.
Results:
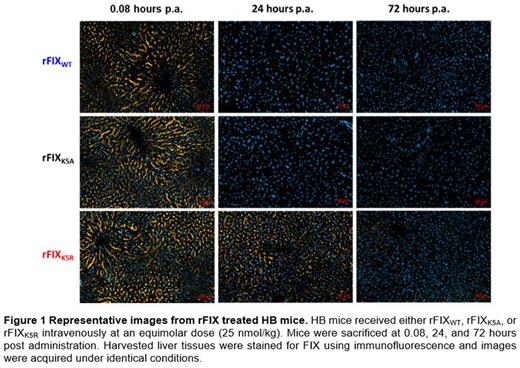
PK studies in HB mice showed that the total exposure was higher for the rFIXK5A mutant which exhibited a dose normalized (dn) AUC0-last of 0.442±0.025 IU/mL*h/IU, followed by lower dnAUC0-last of rFIXWT (0.069±0.023 IU/mL*h/IU) and rFIXK5R (0.056±0.031 IU/mL*h/IU). The predicted dose normalized maximum concentrations (dnCmax) at 5 minutes post administration were comparable between rFIXWT (0.013±0.003 IU/mL/IU), rFIXK5R (0.013±0.001 IU/mL/IU) and slightly higher for rFIXK5A (0.018±0.001 IU/mL/IU). At 5 minutes following intravenous injection, all three rFIX proteins were detected in liver sections with similar mean fluorescence intensities (MFI). However, at 24 hours following intravenous injection, rFIXK5R had higher MFI compared to rFIXK5A and rFIXWT groups (rFIXK5R vs. rFIXWT p<0.001). rFIXK5R was detectable in the liver tissue up to 72 hours even in the absence of circulating FIX antigen levels (Figure 1). Though rFIXK5A was detected in the plasma until 336 hours, the presence in liver tissue was observed only at 5 minutes. Human FIX and murine collagen IV co-staining in liver sections of rFIX treated HB mice showed an overlap of FIX staining mostly with collagen IV-stained regions. However, there were certain liver vascular beds stained specifically for collagen IV with no detectable FIX in that region. To further investigate this, direct binding of FIX to collagen IV was evaluated in SPR and no binding was observed between collagen IV and rFIX wildtype or rFIX mutant proteins. In the tail clip bleeding model, rFIXK5R displayed significant hemostatic protection against bleeding incidence for up to 72 hours post intravenous administration, whereas for rFIXK5A this was only observed at the 15 minutes time point. In the mesenteric artery thrombus model, the time to occlusion of the artery was comparable in both rFIXK5R and rFIXWT treated groups. In contrast, rFIXK5A lacked the ability to form occlusive clots and was comparable to vehicle group. In line with this observation, rFIXWT and rFIXK5R treated HB mice developed significantly larger clots. In contrast, rFIXK5A mutant with decreased binding to components of the EVS exhibited smaller clots compared to rFIXK5R and rFIXWT.
Conclusion: The results of the PK study confirmed a longer exposure of rFIXK5A in plasma compared to rFIXK5R, as expected from decreased binding affinity of rFIXK5A to components of the EVS. The histological evaluations of the harvested liver tissues confirmed a longer accumulation of rFIXK5R, which is expected to have increased binding affinity to components of the EVS. The efficacy studies revealed that the ability of FIX to bind to components of the EVS has an impact on the hemostatic response in HB mouse models. Using two different in vivo models of hemostasis, we demonstrate that mutated rFIX protein with enhanced binding to components of the EVS (rFIXK5R) confers prolonged hemostatic efficacy while the duration of efficacy of rFIXK5A was relevantly shorter after intravenous administration of the recombinant proteins.
Disclosures
Knoll Machado:CSL Behring Innovation: Current Employment. Peil:CSL Behring Innovation GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Kraushaar:CSL Behring Innovation GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Claar:CSL Behring Innovation GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Mischnik:CSL Behring Innovation GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Herzog:CSL Behring Innovation GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Nolte:CSL Behring Innovation GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Bielohuby:CSL Behring Innovation GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Pestel:CSL Behring Innovation GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Ponnuswamy:CSL Behring Innovation GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.